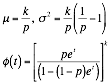Discrete Probability Distributions
|
Name |
Experiment |
Probability Mass Function (pmf), p(x) |
Mean |
Comments |
|
Discrete Uniform |
Equally likely k different values |
|
|
|
|
Bernoulli |
¥ two possible outcomes
|
|
|
|
|
Binomial |
¥ two possible outcomes ¥ fixed number of trials (n) ¥ ¥ independent trials |
X=the number of
successes out of n trials
x=0,1,É,n |
|
¥ Let
|
|
Negative Binomial |
¥ two possible outcomes ¥ no fixed number of trials ¥ ¥ independent trials |
X=the number of
trials at which the kth success occurs.
x=k,k+1,É |
|
¥ If k=1 then it is called a geometric distribution. This
distribution is memoryless. ¥ For the geometric distribution
|
|
Hypergeometric |
¥ N individuals in the population ¥ two possible outcomes M=number of successes in the population ¥ n individuals are selected without replacement |
X=the number of
successes out of n trials
|
|
¥ used when we sample without replacement |
|
Poisson |
¥ counts number of events in one unit ¥ probability that an event occurs in one unit is same for
all units ¥ the number of events in units are independent |
X=the number of
times an event occurs in one unit
|
|
¥ Poisson Approximation to Binomial If X has Bin(n,p)
|
|
Multinomial |
¥ k possible outcomes ¥ fixed number of trials (n) ¥ ¥ independent trials |
XI=outcomes
of the ith kind.
|
||
|
Multivariate
Hypergeometric |
¥ N individuals in the population ¥ k possible outcomes Mi=number
of kind i in the population ¥ n individuals are selected without replacement |
XI=outcomes
of the ith kind.
|
||