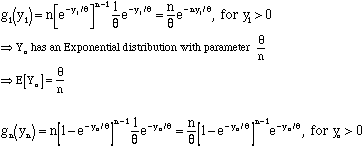INTRODUCTION TO MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS
MATH. 2611
SOLUTIONS TO THE THIRD MIDTERM EXAMINATION
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
Chapter 6: Continuous Distributions
1.
Suppose that the time interval between arrivals of busses to a particular stop is a random variable X (in hours) with exponential distribution and parameter q=30.![]()
![]()
2.
Suppose that X has a uniform distribution with parameters a and 2a. What is the probability that it will take a value less than 3a/2.![]()
3.
Suppose that the number of days X between successive calls to a 24-hour "suicide hotline" has an exponential distribution with q=2.![]()
![]()
4.
Suppose that X has an exponential distribution with parameter q. Find the probability that it will take a value less than -qln(0.9).![]()
5.
Suppose that the average calculus GPA (X) at a university is normally distributed with mean 2.2, and 95% of the time, the GPA is between 1.6 and 2.8. Find the standard deviation of X.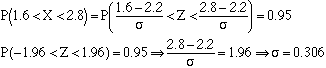
6.
A random variable has a normal distribution with s=10. If the probability that the random variable will take on a value less than 82.5 is 0.8212, what is the probability that it will take a value greater than 58.3?(HINT: Find the mean
m first.)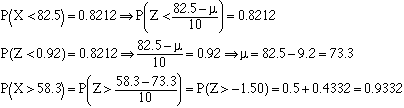
7.
Suppose that X has a Normal distribution with mean 40. For what value of sigma isP(20¾X¾60)=0.50.
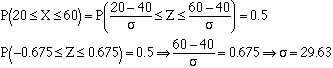
8.
The personnel department of a large corporation gives two aptitude tests to job applicants. One measures verbal ability; the other, qualitative ability. From many year’s experience, the company has found that a person’s verbal score, Y1, is normally distributed with mean 50 and standard deviation 10. The quantitative scores, Y2, are normally distributed with mean 100 and standard deviation 20, and Y1 and Y2 appear to be independent. A composite score is assigned to each applicant, whereY=3Y1+2Y2.
To avoid unnecessary paperwork, the company automatically rejects any applicant whose composite score is below 375. What is the chance that an applicant will fail the screening test?
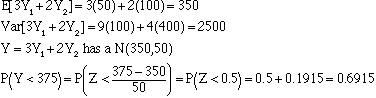
Chapter 8 (Sampling Distribution of the Mean)
1.
A random sample of size 64 is taken from a normal distribution with m=51.4 and s=6.8. What is the probability that the mean of the sample will exceed 52.9?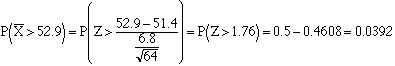
2.
A random sample of size n=225 is to be taken from an exponential distribution with q=4.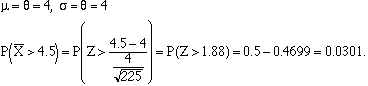
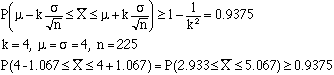
3.
A random sample of size 100 is taken from a normal distribution with m=12 and s=6. What is the probability that the mean of the sample will fall between 7 and 17?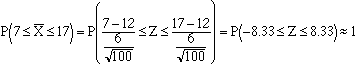
Chapter 8: Chi-Square, t, F distribution
1.
Let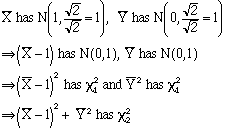
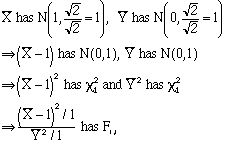
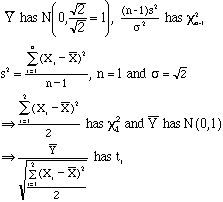
d. Find ![]() .
.
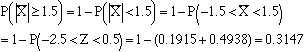
2.
Suppose that X1 has a Normal distribution with m1=2 s12=9, X2 has a Normal distribution with m2=1 s22=4, and X3 has a Normal distribution with m3=3 s32=25 . Assume that X1 , X2 and X3 are independent.What is the distribution of 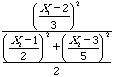 ?
?
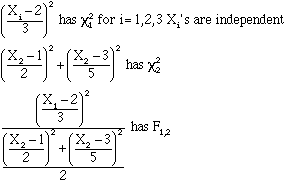
TABLE USE PROBLEMS:
3. If ![]() and
and ![]() are the variances of independent random samples of size
are the variances of independent random samples of size ![]() and
and ![]() from a standard normal distribution, find
from a standard normal distribution, find
a. ![]()
![]()
b. ![]()
![]()
Order Statistics
1. Find the sampling distribution of smallest and largest order statistics (Y1 and Yn) for a sample of size n from a population having an exponential distribution with q. Find the mean and variance of the smallest order statistics. (HINT. Look at the functional form of pdf and compare it with the well known distributions.)