Designed by Engin A. Sungur
Lesson 8:
Contents
This eight lesson covers ...
Objectives
After completing this lesson, you should be able to learn the following:
|
8. INFERENCE FOR COUNT DATA
8.1 Inference for a single proportion
- Constructing confidence intervals for proportions
- Determination of the Sample size
- Carrying out significance tests for proportions
8.2 Comparing two proportions
- Constructing confidence intervals for the difference between proportions
- Carrying out significance tests for the difference between proportions
|
Reading Assignment
Read chapter 8 in Introduction to the Practice of
Statistics.
Activities
Let Us Toss a Coin
Key Terms
Chapter 8
- sample proportion(s) versus population proportion(s)
- confidence interval
- confidence coefficient
- confidence level
- margin of error
- null hypothesis
- alternative hypothesis
- one-sided test
- two-sided test
- P-value
- Type I error
- Type II error
- significance level of a test
- power of a test
- the test being significant
- pooled estimate of the common proportions
- relative risk
Chapter 8: Study Questions
- What is the difference between the sample and population proportion??
- What is the difference between statistical procedures for one
proportion and two proportions problem?
- Which table do you use to carry out the procedures?
- What is the reason that t-distribution is not used?
- Why is the standard error of the p^ calculated differently for the
confidence intervals and significance tests?
- Why do we need to get the pooled estimate of the common proportions?
Chapter 8: Study Notes
To complement your text, we will present the following tables that may
help you to put every thing you have learned together.
For a test of hypothesis problem always go over the following steps
- Set up your null and alternative hypothesis
- Select the significance level of the test
- Decide which test statistics you need to use
- Find the value of your test statistic and P-value
- Write down your decision
If you want to make an inference related with a single population
proportion use the following table.
Inference on Population Proportion
Test Of Hypothesis
|
Null & Alternative Hypothesis |
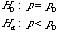
|
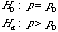
|
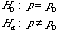
|
|
Significance Level Of the Test |
a |
a |
a |
|
Test Statistics |
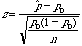
|
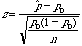
|
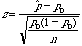
|
|
p-value |
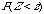
Table A |
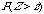
Table A |
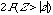
Table A |
|
Decision |
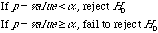
|
Confidence Interval
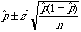 (get the z*
value from the Table D)
(get the z*
value from the Table D)
Determination of the Sample Size
If you have an initial guess p*:
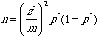 (get the z*
value from the Table D, m is the margin of error)
(get the z*
value from the Table D, m is the margin of error)
If you do not have an initial guess:
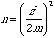
If you want to make an inference related with comparing two population
proportions use the following table.
Inference on Difference Between
Population Proportions
Test Of Hypothesis
|
Null & Alternative Hypothesis |
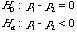
|
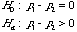
|
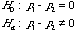
|
|
Significance Level Of the Test |
a |
a |
a |
|
Test Statistics |
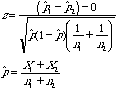
|
|
p-value |
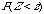
Table A |
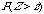
Table A |
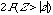
Table A |
|
Decision |
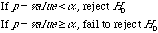
|
Confidence Interval
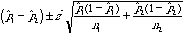 (Get z* value
from the Table D)
(Get z* value
from the Table D)
Written Assignment
Do the following assignment. The problems listed are from
"Introduction to the Practice of Statistics".
When you have worked on the problems and are ready to turn in
your findings, click the assignment
link below. It will take you to a template where you can fill in your
answers to the questions. When you are
finished entering your answers, click the submit button, you will be
given the location of your completed web
page. You may check your assignment responses with your browser at any
time, and submit a revision at any
time before the due date of the assignment. The due date is Monday
August 16..
|
SECTION 8.1.Exercise 8.4, 8.12, 8.18, 8.20 (page
596-599) |
|
SECTION 8.2.Exercises 8.28, 8.34, 8.40, 8.44 (pages
609-613) |
|
CHAPTER EXERCISES. 8.56 (page 617)
|
Lesson Submission 7
Assignment #7.
Internet Links
Each day you go online, be sure to check out the Random
Statistical Quote for the Day


![]() (get the z*
value from the Table D)
(get the z*
value from the Table D)![]() (get the z*
value from the Table D, m is the margin of error)
(get the z*
value from the Table D, m is the margin of error)![]()
![]() (Get z* value
from the Table D)
(Get z* value
from the Table D)